Jeff Gundlach On Fed Policy
This post was originally published on
The Federal Reserve has signaled that there will be no interest rate cuts in the immediate future, particularly not by March. This forecast aligns with the inflation model predictions, which suggest a stall in the declining inflation rate. This situation may dampen market enthusiasm, which had previously anticipated imminent rate cuts.
Inflation and Market Response
Inflation, which had been expected to reduce, is now likely to plateau, thereby delaying the anticipated rate cuts. The market's previous euphoria over potential cuts has been tempered by this development. Risk assets, including stocks and high-yield bonds, had reached high levels of enthusiasm, with valuations returning to early 2022 figures. However, the Fed's candid approach, especially regarding a March rate cut, has led to a recalibration of expectations.
Employment and Economic Growth Risks
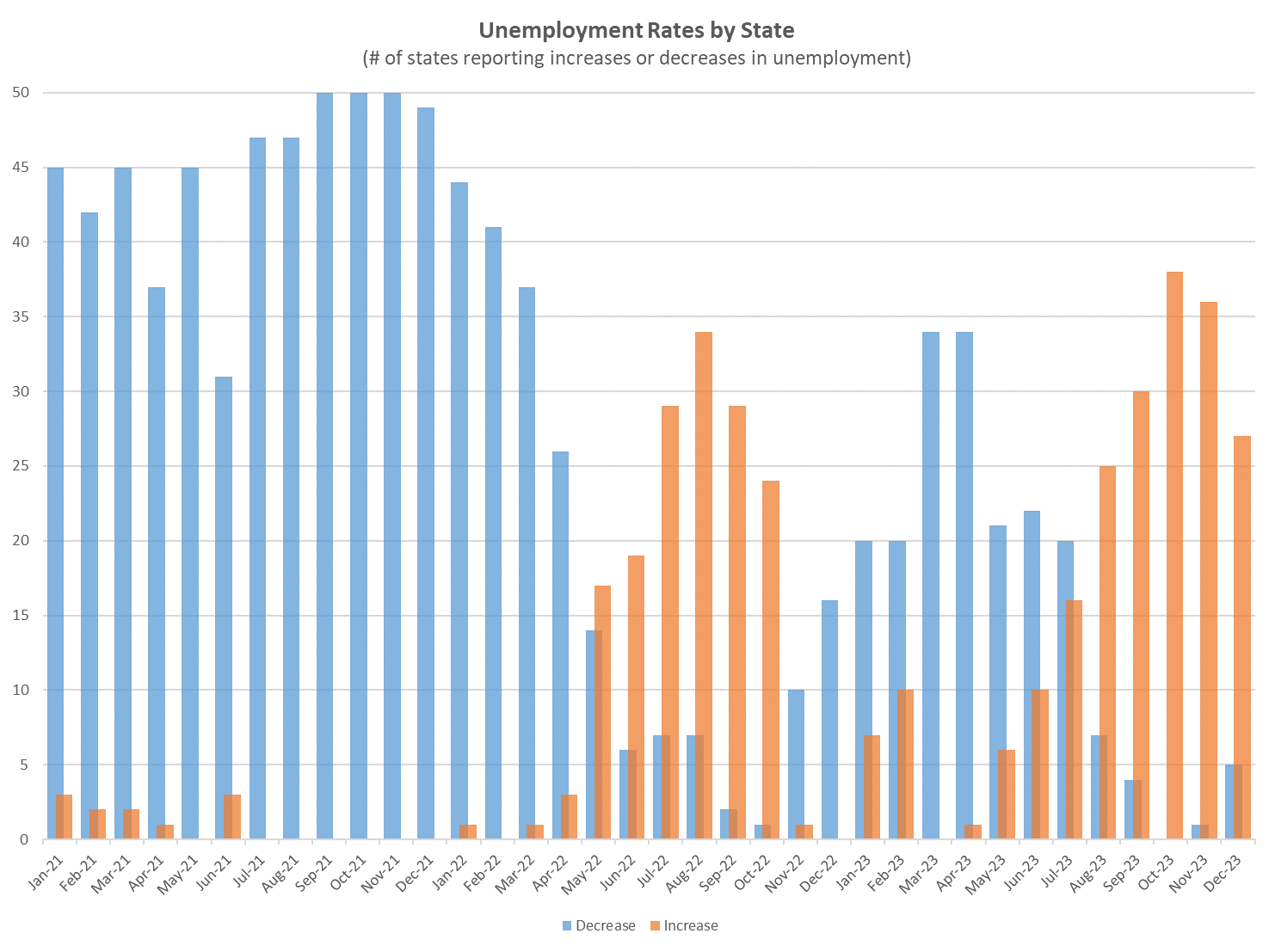
Despite favorable headline establishment surveys on the employment market, other indicators suggest increasing unemployment rates across states. A majority of states have reported a rise in unemployment over the last six months, presenting a discrepancy with the national unemployment rate. Leading indicators such as continuing claims and temporary employment are on the rise, while the quits rate has returned to pre-pandemic levels.
Interest Rates and Bond Market
The Federal Reserve is maintaining a real interest rate on Fed funds, which poses risks to economic growth. The bond market, particularly the short end, has seen a decrease in yield, yet the market should not expect a rate cut in the next few months. The market had heavily priced in a March rate cut, affecting valuations across risk markets.
Inflation Indicators and Future Cuts
There are some optimistic signs for future inflation trends, such as the Producer Price Index (PPI) remaining negative year-over-year, and import and export prices, which are not subject to adjustments, also showing negative figures year-over-year. Despite this, a rate cut delay is anticipated, and the market is less euphoric as a result.
Federal Reserve's Political Neutrality and Decision Making
The Federal Reserve's decision-making process is influenced by its dual mandate, and although there is speculation about its political motivations, especially in relation to the upcoming presidential election, the focus remains on achieving an inflation rate that approaches or stays near 2%. The Fed's higher-for-longer stance may result in a weakened economy and necessitate rate cuts later in the year.
Commodity Prices and Economic Indicators
Commodity prices, tracked by the Bloomberg Commodity Index, show a protracted downtrend, indicating a possible weak global economy. Geopolitical tensions have not significantly impacted oil prices, suggesting that commodity and oil demand may be waning.
Recession Predictions and Market Strategy
There is an expectation of a recession in 2024, with concerns about the valuation of risk assets and credit markets. The bond market, particularly treasury bonds, may present attractive opportunities, especially if the Fed's policies engineer a lower inflation rate. A defensive stance is recommended, with a preference for cash and defensive bonds as a hedge against potential market downturns.
Banking System Concerns
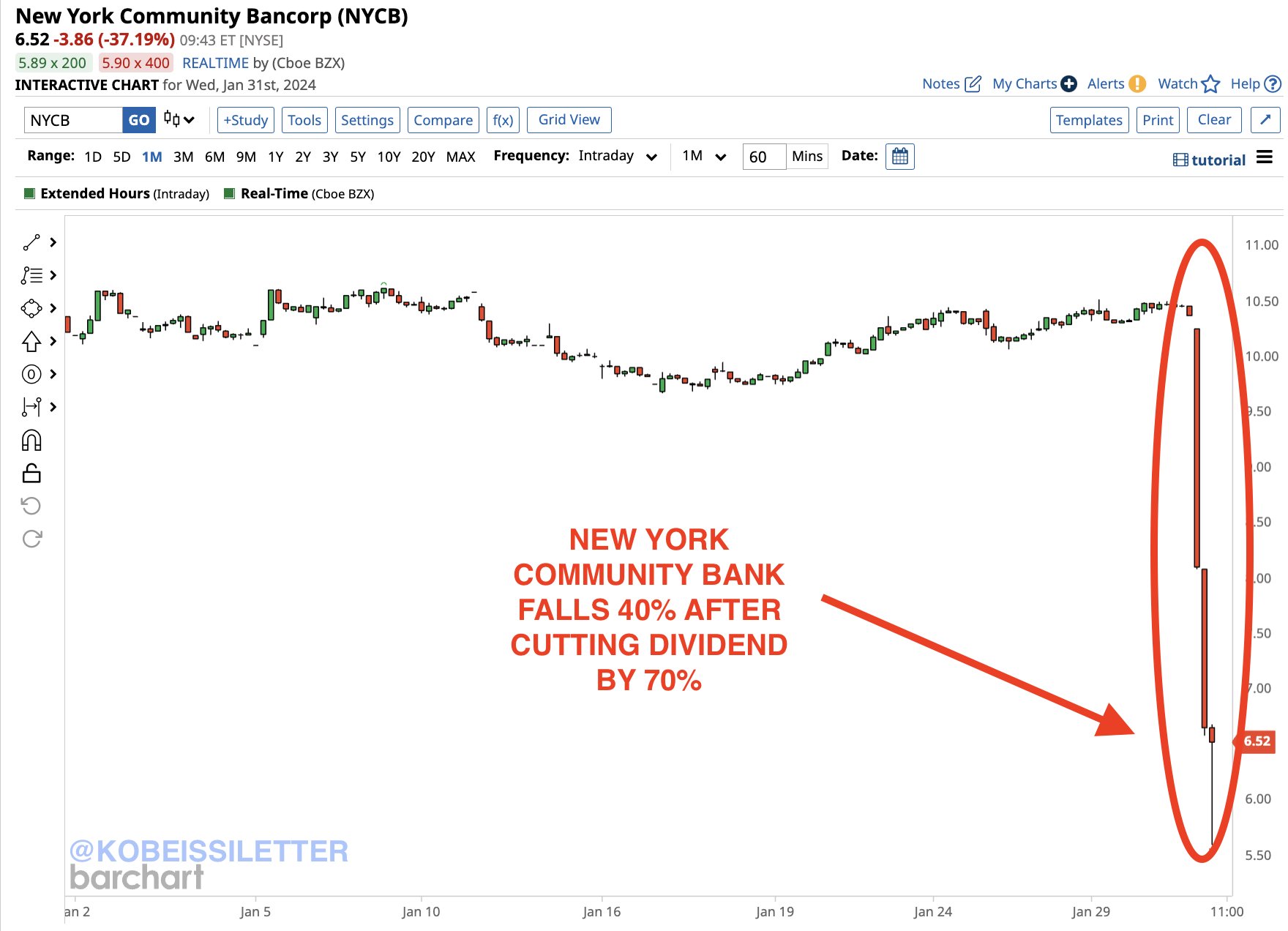
The regional banking system may face challenges, especially in the context of commercial real estate. Recent issues with New York Community Bank highlight the potential for broader concerns that could influence the Fed's actions.
Deficit and Fiscal Policy
The deficit issue, while not immediately at the forefront of market concerns, presents longer-term risks. Rising interest costs and the potential insolvency of Medicare and Social Security within the decade are serious considerations that could shape future fiscal policy.
The Dollar and Foreign Markets
The dollar is expected to remain stable or strengthen as rate cuts are postponed. However, in the event of a recession, the dollar's behavior may differ from past trends, potentially weakening due to policy responses. India is highlighted as a robust economy with investment opportunities, particularly in its equity market.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve's stance on keeping interest rates high for an extended period may lead to a weakened economy, potentially culminating in a recession in 2024. Investors are advised to adopt a defensive approach, focusing on cash, treasury bonds, and cautious engagement with emerging markets. The overarching sentiment is one of caution, particularly given the potential for an economic slowdown and its implications for various asset classes.